Scalable data architecture to create seamless digital banking experiences
Reading Time: 5 minutes

The need for seamless banking experiences and personalized services is driving banks to leverage data and analytics for effective decision-making. According to a recent survey, a staggering 75% of consumers are inclined to gravitate toward a bank that goes the extra mile to offer personalized services. Traditional banking models, often characterized by rigid, siloed systems, are proving to be increasingly inadequate in meeting these evolving demands. Legacy infrastructures struggle to handle the data deluge, resulting in fragmented customer experiences and missed opportunities for engagement.
According to Forbes, global data is set to double every 12 hours by 2025. It means all businesses including banks will have to deal with increasingly large volumes of data in the coming years.
This blog highlights the pivotal role of architecting scalable data solutions that drive seamless, personalized banking experiences.
The principles of a scalable architecture
Scalable data solutions hold the promise to redefine customer experiences in banking. In data architecture, scalability involves orchestrating systems to adeptly manage rising workloads while preserving performance and reliability. This entails prioritizing horizontal scaling, ensuring fault tolerance, implementing load balancing, efficient data partitioning, and leveraging distributed computing to maintain system agility and resilience.
- Modularity and decoupling of components: At the heart of a scalable architecture lies the concept of modularity and the decoupling of components. By breaking down complex systems into modular components, banks can enhance their flexibility and agility. This approach enables them to isolate and address specific issues without disrupting the entire system. Additionally, decoupling components allows for independent scaling and facilitates better maintenance.
- Elasticity and resource optimization: Scalable architecture emphasizes the need for elasticity and resource optimization which enables banks to dynamically adjust resources in response to fluctuating workloads and demands. Through automated scaling mechanisms, the system can seamlessly allocate resources in real-time, ensuring optimal performance during peak periods and conserving resources during lulls.
- Fault tolerance and high availability: Even a brief system outage can have far-reaching consequences, making fault tolerance and high availability paramount. A scalable architecture ensures that the system remains resilient in the face of failures, mitigating the impact of negative customer experiences. By implementing redundant components and failover mechanisms, banks can sustain operations in the event of hardware failures or other unforeseen issues.
- Data partitioning and sharding for performance: Effective data management lies at the core of a scalable architecture. Data partitioning and sharding enable banks to distribute and manage large datasets across multiple servers, enhancing overall performance and response times. By segmenting data based on specific criteria, such as customer demographics or transaction types, banks can optimize data access and retrieval. This approach not only enhances performance but also lays the groundwork for future scalability as data volumes continue to grow.
- Unified vocabulary: Establishing a common vocabulary is critical for effective data governance and discovery. It involves creating a shared vocabulary for terms like “customer,” “transaction,” and “risk” in banking to ensure consistent interpretation and usage of these terms across different banking domains. A centralized data catalog further supports data discovery, allowing teams to easily locate and understand relevant datasets.
- Minimizing data redundancy: Banks can eliminate data copies and movement by focusing on minimizing redundancy in data storage. Rather than duplicating customer information across multiple databases, a centralized customer data repository should be established. By avoiding unnecessary data copies, banks enhance data integrity and minimize the complexities associated with data movement.
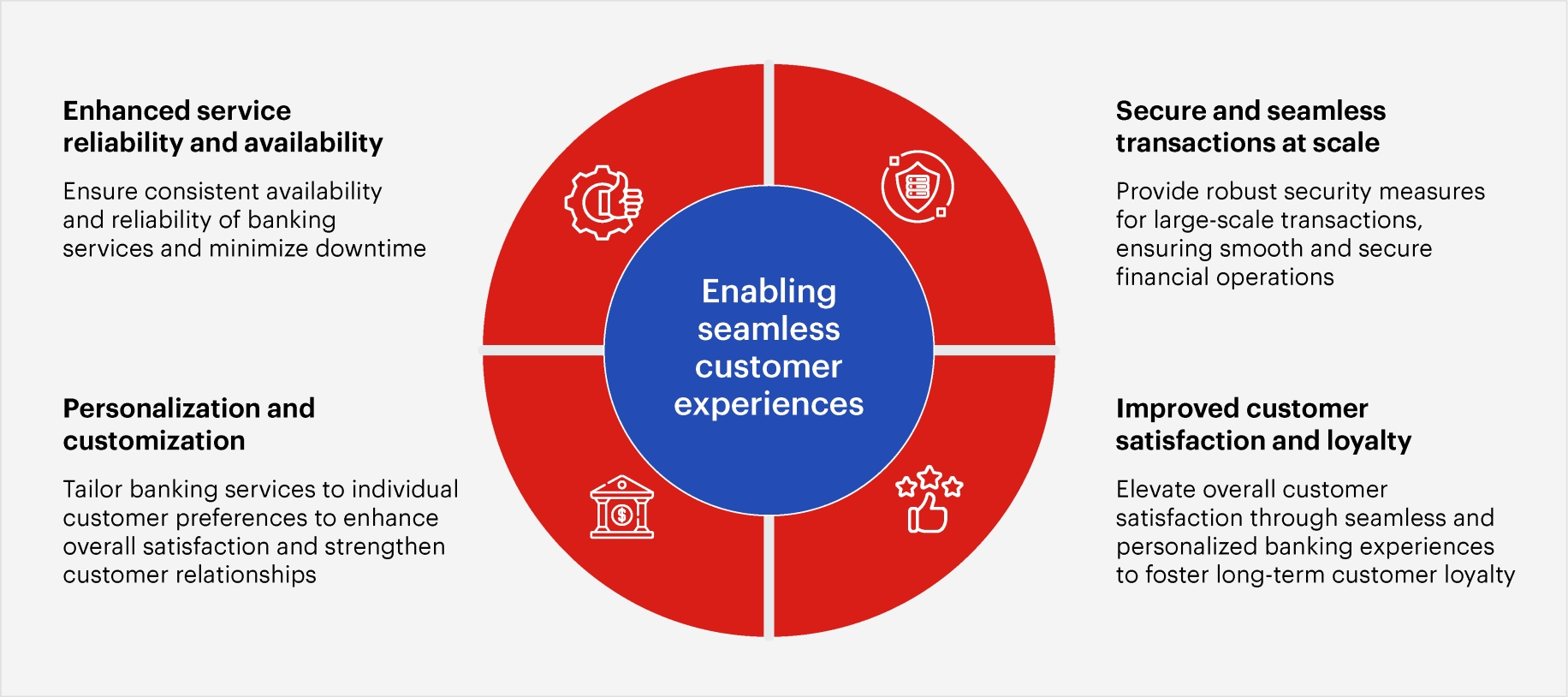
Scalable architecture for customer experiences in Banking
The intricate interplay between a robust scalable framework and the dynamic demands of customers underscores the need for banks to prioritize adaptability and innovation. Here, we elucidate the need for scalable architecture within the banking sector.
| What is MLOps? |
|---|
| MLOps, the innovative fusion of machine learning and operational processes, plays a pivotal role in empowering scalable data solutions for banks. Key components include integrating ML models for personalized services and risk management, automating data pipelines for efficiency, and utilizing MLOps for real-time data processing. This fosters proactive responses to market changes and customer needs that can in turn cultivate trust and loyalty among customers. |
How Sigmoid builds scalable analytics for banking and financial services
Sigmoid leveraged advanced financial analytics to craft scalable financial products that address the specific needs of our customer, a prominent FinTech enterprise servicing a vast network of banks and credit unions globally.
| Situation | Solution | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| The customer, a leading FinTech enterprise serving more than 15,000 banks and credit unions worldwide, sought to develop data products that should lead to new revenue streams. They faced the challenge of developing a scalable and configurable data platform for their corporate, commercial, and retail banking clients which is readily available and delivers data-driven insights for growth and innovation. | Sigmoid designed a scalable data mesh architecture on GCP to consolidate data from multiple sources and develop data products for new revenue opportunities. We built the reference architecture to implement a digital banking data platform that combined data engineering, DataOps, and advanced analytics. A lean, config-driven approach was employed for swift integration, data pipelining, warehousing, and dashboarding. |
|
Conclusion
The strategic implementation of scalable data solutions is the cornerstone of creating seamless banking experiences in modern banking. By prioritizing the principles of modularity, elasticity, fault tolerance, and data partitioning, banks can effectively navigate the evolving customer expectations. Integrating MLOps further enhances the capability to harness sophisticated algorithms, streamline data pipelines, and provide real-time data processing and analysis, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction and sustainable growth. Through a proactive embrace of scalable architecture, banks can not only meet but exceed the demands of the digital-first and customer-centric banking industry.
Featured blogs
Subscribe to get latest insights
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI
Featured blogs
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI






