Unlocking procurement transformation with AI and advanced analytics
- Chapter- 1 Introduction
- Chapter- 2 The new procurement reality: Navigating a dynamic and complex landscape
- Chapter- 3 Evolution of the procurement organization
- Chapter- 4 Key procurement objectives for 2026 and beyond
- Chapter- 5 State of technology in procurement
- Chapter- 6 Emerging technologies shaping the future of procurement
- Chapter- 7 Key steps for building a high-performing procurement function
- Chapter- 8 Building the procurement function of the future
1. Introduction
Procurement is at an inflection point. Once regarded as a transactional back-office function, it is now being redefined by AI-driven innovation. From generative AI in procurement delivering real-time insights to agentic AI in procurement autonomously managing sourcing cycles, the function is rapidly evolving into a strategic pillar for resilience, efficiency, and growth. This transformation is accelerating the rise of autonomous procurement, powered by intelligent analytics and procurement automation that streamline operations, strengthen supplier relationships, and enhance agility in volatile markets.
Read on to know how AI and advanced analytics are reshaping the procurement lifecycle and a few practical steps leaders must take to build a high-performing, future-ready procurement function.
2. The new procurement reality: Navigating a dynamic and complex landscape
Procurement leaders today operate in a volatile environment shaped by:
- Macroeconomic and geopolitical instability: Rising inflation, supply disruptions, and dynamic regulatory environments.
- Supply chain realignment: Increased focus on local sourcing, nearshoring, and supplier diversification.
- Sustainability and inclusion: Growing expectations around responsible sourcing, ESG compliance, and supplier diversity.
- Technology disruption: Rapid advancements in AI, LLMs, and automation in procurement are driving the need for smarter processes
According to a report published in the EY Global CPO survey 2025, rising inflation and challenging market conditions, emphasis on supply chain risk management and resilience and a rise in regulatory changes and compliance requirements were ranked as the top market trends impacting procurement strategies & operating models globally. [Source: EY]
3. Evolution of the procurement organization
For decades, procurement was largely viewed as an administrative function, tasked with reducing costs through price negotiations, managing suppliers, and enforcing contractual compliance. These traditional models often relied on manual, fragmented processes that limited procurement’s influence and overlooked opportunities to optimize operations, drive supplier-led innovation, or align sourcing strategies with broader business goals.
Today, leading organizations recognize procurement as a strategic business partner capable of delivering measurable impact far beyond cost savings. Modern procurement teams are instrumental in enabling value creation, competitive differentiation, supply chain agility, and risk management in an increasingly VUCA world. This transformation has been driven by the convergence of shifting business priorities, evolving operating models, and the adoption of advanced analytics in procurement.
3.1. Procurement operating models: From centralization to hybrid agility
Global procurement functions operate in diverse organizational contexts, with structures tailored to business size, geographic footprint, and industry dynamics. The three primary models are:
- Centralized Procurement – All procurement decisions and activities are consolidated under a single, specialized team or department, enabling consistent policies, economies of scale, and standardized supplier management.
- Decentralized Procurement – Responsibility for procurement is distributed across business units or regions, allowing for local decision-making and responsiveness to market conditions.
- Matrix (Center-led) Procurement – A hybrid model that combines centralized policy and governance with decentralized execution, balancing strategic control with local flexibility.
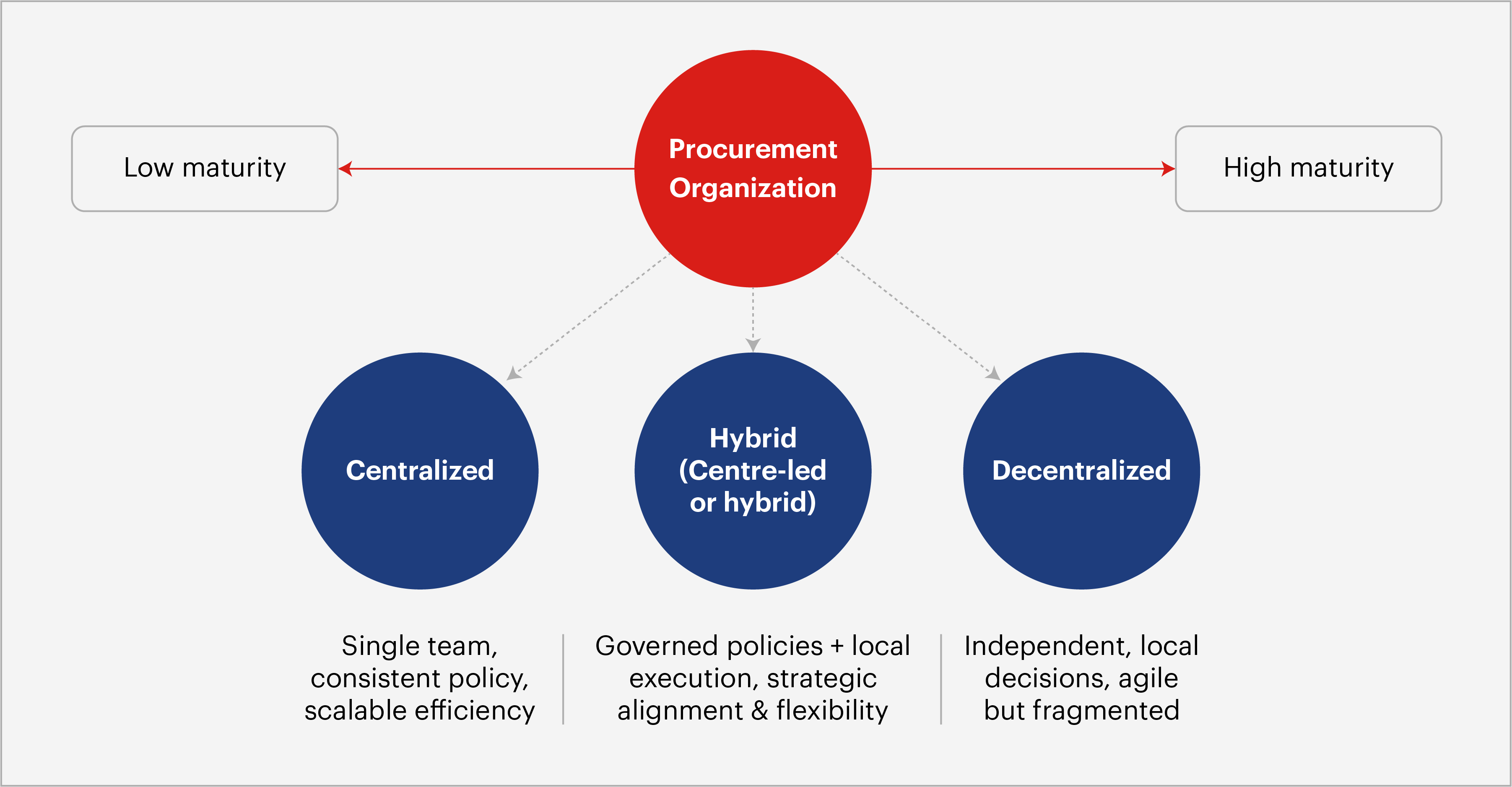
Fig.1. Structure of a procurement organization
3.1.1. Functional layers of modern procurement organizations
Most mature procurement models share common operational layers that define roles, responsibilities, and strategic influence:
- Leadership and governance centres: Core strategic groups responsible for defining procurement policies, frameworks, and transformation roadmaps, as well as driving internal reporting and business analytics.
- Centers of Excellence (CoEs): Category management and strategic sourcing teams tasked with delivering procurement objectives, managing supplier risk and performance, and supporting decentralized teams on specialized sourcing requirements.
- Centre of scale and operations: Typically managed by decentralized business units, focusing on tactical sourcing, contract execution, and supplier relationship management to ensure continuity of supply.
In addition, distributed teams whether embedded in business units or located in Outsourced/ Global Shared Service/ Support Centres manage two critical areas:
- Transactional procurement processes: Activities such as spot buys, PR-PO conversions, invoice matching and exception handling, order tracking, expedition, and logistics/customs clearance.
- Enabling functions: Backend support such as master data management (MDM), catalog management, and other operational enablers that ensure process accuracy and consistency.
3.1.2. Technology-enabled Transformation
While many organizations still operate within similar structural models, technology has become the decisive factor in procurement maturity. New-age tools, from cloud-based procurement suites and advanced analytics platforms to AI-powered sourcing agents, are helping procurement teams:
- Streamline transactional processes through automation in procurement
- Enhance supplier performance visibility using technology procurement best practices
- Enable predictive risk management
- Drive data-informed decision-making at both strategic and tactical levels with IT
By leveraging these capabilities, procurement is moving from a cost-control mindset to becoming a value-creation engine, capable of contributing directly to business growth, resilience, and innovation.
4. Key procurement objectives for 2026 and beyond
Procurement leaders are entering 2026 with unprecedented challenges and opportunities. Inflationary pressures, shifting supply chain models, sustainability commitments, and rapid advances in AI are reshaping expectations from the function. No longer limited to cost management, procurement is now tasked with driving resilience, enabling innovation, and aligning closely with enterprise-wide transformation goals.
To deliver on this expanded mandate, organizations must set clear objectives that balance near-term efficiency with long-term value creation including:
- Cost reduction and spend optimization: Continuing to deliver measurable savings remains a priority in the face of inflationary pressures and tightening margins. Strategic sourcing, category management, procurement automation, and spend analytics are central to achieving these goals without compromising value.
- Risk management and supply chain resilience: Geopolitical volatility, trade policy changes, and supply chain disruptions are accelerating the need for proactive risk identification and mitigation. Leveraging procurement best practices helps to safeguard continuity through diversified sourcing, nearshoring, and friend-shoring strategies.
- Sustainability and responsible sourcing: Growing consumer and regulatory expectations are pushing procurement to lead ESG initiatives and adopt technology procurement best practices that ensure supplier compliance with sustainability standards and foster diversity and inclusion across supplier networks.
- Digital transformation and AI adoption: The most transformative priority is the integration of next-generation technologies such as Generative AI in procurement and Agentic AI in procurement to enable autonomous decision-making, enhancing process efficiency, and unlocking new forms of competitive advantage.
Collectively, these objectives reflect the elevated role of procurement as a strategic enabler, driving cost efficiency, supply assurance, compliance, and innovation in equal measure.
5. State of technology in procurement
In 2025, technology has transformed procurement from a transaction-based function into a digitally connected, insight-driven capability embedded in enterprise strategy. The focus is no longer just on digitizing existing processes, but on reimagining the procurement lifecycle for speed, transparency, and intelligence.
- Integrated digital platforms now unify sourcing, contracting, supplier management, and payment processes in a single environment with IT procurement best practices. This consolidation eliminates data silos, accelerates cycle times, and provides procurement teams with real-time visibility into supplier catalogs, spend patterns, and approval workflows.
- Cloud-enabled procurement extends accessibility and collaboration across geographies, enabling distributed teams to manage procurement activities securely and efficiently. Modular cloud solutions allow organizations to scale capacity, integrate with external data sources, and pivot strategies quickly in response to market shifts.
- Blockchain applications are enhancing trust and compliance by creating immutable records of transactions, enabling instant traceability of materials, and validating supplier credentials, particularly critical for highly regulated sectors such as pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and food manufacturing.
- Real-time analytics dashboards give procurement leaders the ability to monitor supplier performance, contract adherence, and category spend with precision. These insights drive proactive decision-making and help identify cost-saving opportunities before they are lost.
- AI-driven automation has moved beyond simple task execution to orchestrating complex procurement workflows. Intelligent algorithms now assist with demand prediction, supplier shortlisting, and compliance monitoring, while generative AI in procurement and autonomous agents deliver context-specific recommendations and handle repetitive, high-volume activities.
The result is a procurement function that is not only more efficient but also more agile and resilient, capable of anticipating risks, responding to market volatility, and contributing directly to enterprise growth.
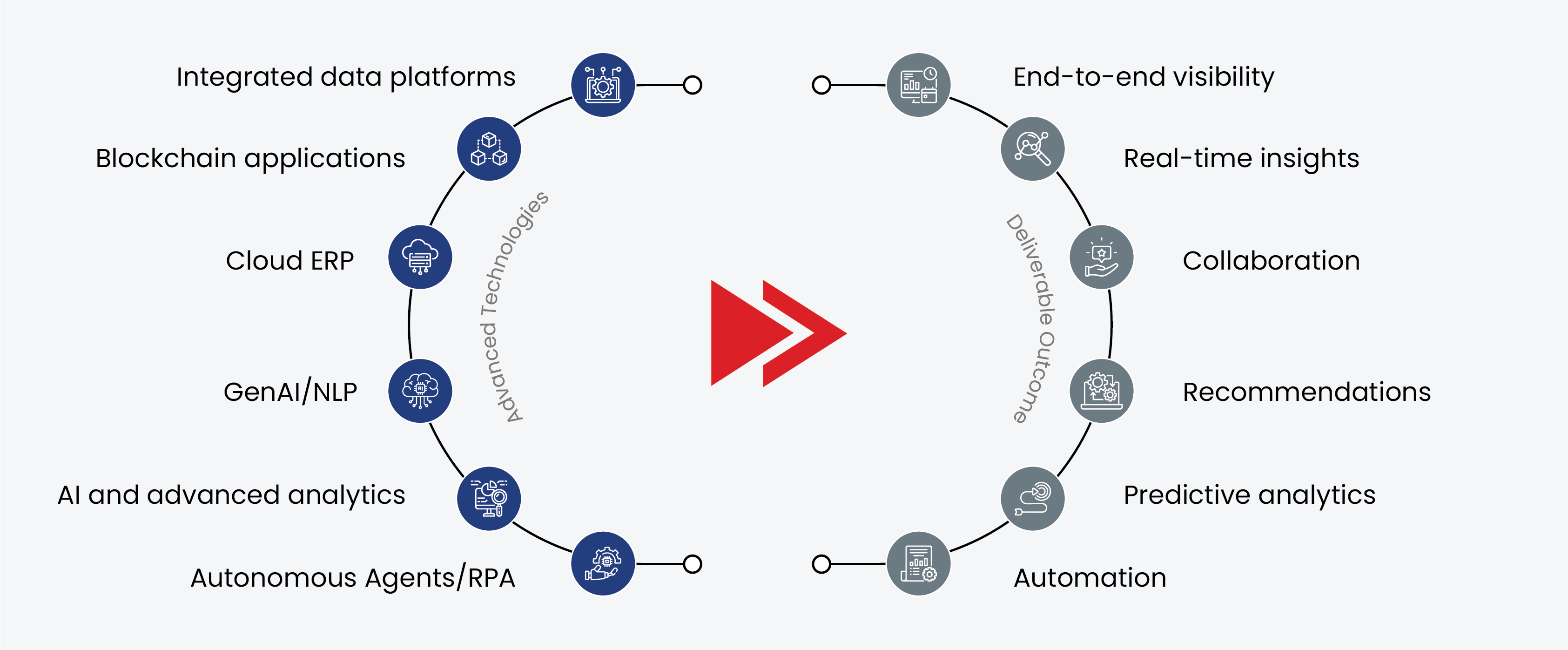
Fig.2. Impact of modern technologies in procurement function
6. Emerging technologies shaping the future of procurement
Procurement is on the brink of another major leap forward with a wave of next-generation technologies that enable not just process improvements but also how it delivers value to business:
- Advanced analytics for predictive and prescriptive insights: Expanding access to diverse, multi-source procurement data (from internal ERP transactions to external market and risk intelligence) is unlocking a richer, more connected view of the supply landscape. AI and ML-driven analytics models now power scenario simulations, risk forecasting, and should-cost analysis, enabling procurement leaders to make proactive, evidence-based decisions in sourcing, contracting, and negotiation.
- Generative AI for knowledge synthesis and decision support: GenAI or large language models, is bringing a new dimension of autonomy and intelligence to procurement. Beyond summarizing and generating content, these systems can converse in natural language to surface relevant market data, draft RFPs, extract insights from contracts, and contextualize supplier performance data. This, in turn, reduces cycle times and enhances decision quality.
- AI agents and agentic networks for autonomous operations: Building on GenAI, autonomous AI agents function as digital procurement team members. They can execute end-to-end workflows, from supplier identification and qualification to contract execution, without human intervention for routine categories. These agents can continuously monitor risk signals, implement mitigation strategies in real time, and autonomously handle high-volume transactional tasks, freeing human teams to focus on strategic activities.
- Digital twins for supply chain resilience: Procurement-focused digital twins create a dynamic, real-time replica of the supply network, including suppliers, manufacturing sites, logistics nodes, and transport routes. This virtual model enables “what-if” scenario testing to evaluate the impact of disruptions, optimize sourcing strategies, and preempt supply constraints before they affect operations.
- Low-code and No-code platforms for rapid adoption: Low-code and no-code technologies are empowering procurement and IT teams to create and customize workflows, dashboards, and integrations without deep technical expertise. This accelerates the deployment of tailored solutions, supports continuous improvement, and enhances agility in responding to evolving business and market needs by following technology procurement best practices.
As these technologies converge, procurement’s role will shift from reactive execution to strategic orchestration, where intelligent systems continuously sense, analyze, and act in partnership with human expertise to deliver competitive advantage.
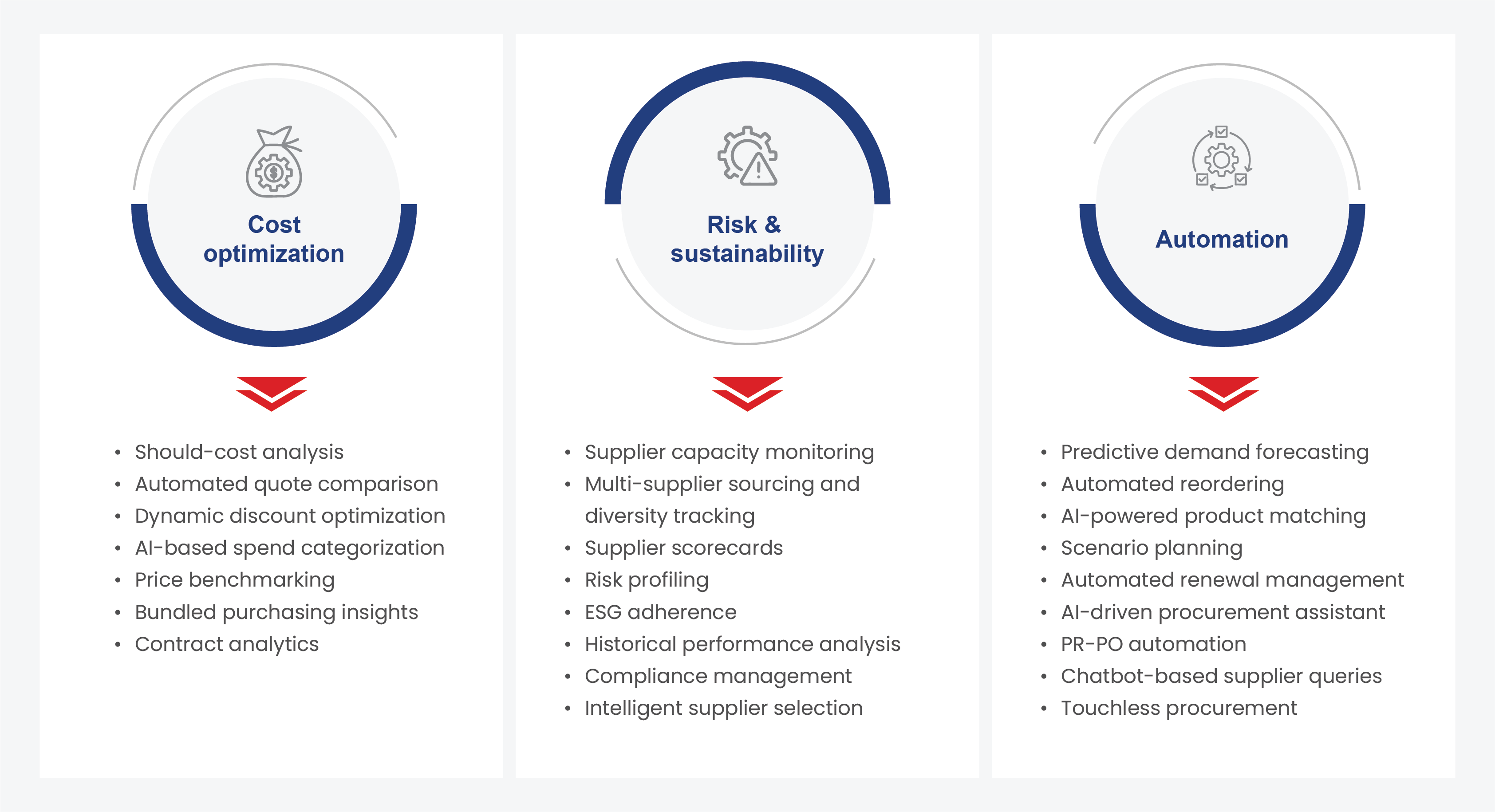
Fig.3. Capabilities for a high-performing procurement function
Case in point: AI-powered autonomous procurement
Sigmoid partnered with a global pharmaceutical major to transform logistics operations using an agentic AI-powered analytics platform. The solution integrated seamlessly with enterprise apps like Microsoft Teams and Power BI, autonomously surfaced cost-saving and optimization opportunities over a conversation chatbot-like interface. This feature enabled procurement and logistics teams to query data and get real-time insights in natural language, bringing advanced analytics into everyday decision-making and transforming daily operations by embedding procurement best practices at scale.
7. Key steps for building a high-performing procurement function
Building a high-performing procurement function in the age of AI requires more than technology adoption. It demands deliberate, structured actions led from the top and bringing holistic transformation of processes, data, talent, and governance.
The following checklist outlines critical steps leaders should take to prepare their organization for this transformation. These actions will help ensure that AI, Generative AI, and Agentic AI deliver sustainable value and position procurement as a core driver of competitive advantage.
8. Building the procurement function of the future
The shift toward autonomous procurement is no longer aspirational; it is already underway. The convergence of Agentic AI in procurement, Generative AI in procurement, and intelligent analytics is transforming procurement into a strategic, insight-driven powerhouse. By adopting procurement best practices, embedding procurement automation, and driving AI-led procurement transformation, organizations can elevate procurement into a high-impact strategic function.
In this new model, AI agents take on high-volume, repetitive activities such as transactional sourcing, compliance checks, and supplier performance monitoring. This frees procurement professionals to focus on innovation, supplier collaboration, strategic negotiation, and enterprise value creation. The result is a symbiotic operating model where human expertise and machine intelligence complement each other to deliver speed, precision, and agility at scale.
To build the procurement function of the future, organizations should:
Organizations that act decisively now will not only reduce costs and manage risk more effectively. Procurement must be seen as a central driver of competitive advantage and long-term business resilience. The autonomous procurement revolution has already begun; don’t get left behind.
About the authors
Biswa Mohan Parida is a Supply Chain Consultant at Sigmoid. He brings over 13 years of experience in supply chain consulting, strategy, and operations. He has led large-scale global supply chain transformation programs, with deep expertise in manufacturing, airlines, CPG, healthcare, and aerospace & defense industries. Biswa specializes in digital procurement transformations, both upstream and downstream, and has delivered measurable outcomes including multi-million-dollar savings, improved spend under management, and enhanced supplier compliance. His experience spans pre-sales and delivery consulting, ERP and source-to-pay system implementations, and advanced supplier risk analytics initiatives.
Shriya Gupta is a Management Consultant at Sigmoid. She brings 6+ years of experience in supply chain, analytics, and strategy consulting across fintech, manufacturing, healthcare, mining, and CPG sectors. She brings strong expertise in automation, product management, and stakeholder engagement, having delivered impactful projects in procurement strategy, cost reduction, predictive analytics, and process optimization.

