Building trustworthy Agentic AI starts with the right guardrails
Reading Time: 5 minutes
Business ecosystem is operating in a new phase of autonomy driven by Agentic AI. Agentic AI refers to AI systems that combine large language models with tools, memory, and planning capabilities, enabling them to take autonomous actions rather than simply generate responses. These AI systems no longer wait for explicit human prompts; they can reason, plan, and act independently to achieve specific goals. Such an evolution holds immense potential for enterprises, enabling intelligent automation, adaptive decision-making, and continuous optimization across business functions.
But autonomy also introduces new layers of complexity and risk. When AI agents can take actions on their own such as interacting with data, systems, and external applications, the margin for error widens. Hallucinations, policy violations, data leakage, or biased decisions can easily emerge in the absence of proper oversight.
To realize the promise of Agentic AI responsibly, organizations must build guardrails that are structured systems of control to define safe operating boundaries for AI agents. Far from limiting innovation, guardrails ensure every autonomous action remains aligned with human intent, enterprise policy, and ethical standards.
This blog explores why guardrails are essential, what the three foundational layers of governance look like, and how enterprise leaders can build frameworks that make agentic AI truly enterprise-ready.
The risks of insufficient guardrails
Agentic AI operates with greater independence, thereby increasing the risk of unintended consequences. Without clear boundaries and monitoring mechanisms, enterprises face risks that can escalate quickly:
- Data breaches or misuse of sensitive information caused by uncontrolled access or poor permissions.
- Model drift and unpredictable decision loops that lead to incorrect or costly outcomes.
- Regulatory non-compliance and reputational damage from unethical or unverified AI actions.
- Loss of stakeholder trust when outputs reflect bias, misinformation, or unsafe recommendations.
Autonomy without accountability can derail enterprise-scale AI transformation. Guardrails serve as the foundation for sustainable innovation while supporting control, consistency, and confidence in every AI-driven decision.
Three layers of guardrails for Agentic AI
1. Technical guardrails
At the base of every agentic system lies a technical control framework that ensures AI actions remain predictable, traceable, and bounded. These guardrails act as the first line of defense against unregulated autonomy.
Key mechanisms include:
- Access and Permissions: Clearly define what systems, databases, and APIs agents can interact with to prevent data leaks or unauthorized actions.
- Quotas and Rate Limits: Control execution cycles to avoid runaway loops, excessive API calls, and escalating operational costs.
- Memory and State Management: Regulate what information an agent can store or recall to prevent persistent data risks and contextual errors.
- Schema Validation: Ensure inputs and outputs conform to predefined formats, preserving data integrity across tools and systems.
- Error Handling and Loop Breakers: Detect recursive reasoning or unintended planning loops early and terminate them safely.
2. Ethical guardrails
As agentic systems begin to act independently, they must also act responsibly. Ethical guardrails define the moral and policy boundaries that prevent harm and maintain public trust. Ethical guardrails help enterprises build AI that is not just functional but trustworthy, transparent, and value-aligned. For leaders, this is the cornerstone of sustainable AI adoption.
Key considerations include:
- Content safety: Monitor and restrict the generation of unsafe, biased, or policy-violating content.
- Truthfulness and Accuracy: Reinforce outputs with retrieval-grounded evidence and fact-checking mechanisms.
- Policy Compliance: Align actions and responses with enterprise ethics, brand voice, and legal frameworks.
- Bias and Fairness Monitoring: Continuously audit outputs for skewed representation or discriminatory behaviour.
- Privacy and Data Protection: Support compliance with global standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and the EU AI Act.
3. Operational guardrails
Operational guardrails bring governance and visibility into the day-to-day functioning of AI agents. They define how systems are monitored, intervened upon, and improved over time. Operational guardrails keep AI ecosystems adaptive and resilient. For leaders, they ensure that human judgment and safety oversight remain integral to every autonomous decision.
Core practices include:
- Observability and Monitoring: Enable real-time tracking of agent decisions, reasoning paths, and system interactions.
- Human-in-the-Loop (HITL): Integrate checkpoints for human review where risk, sensitivity, or uncertainty is high.
- Fallback Mechanisms: Create alternative workflows that take over when AI agents encounter anomalies or policy conflicts.
- Red Teaming and Continuous Evaluation: Simulate adversarial scenarios to stress-test AI resilience.
- Isolation and Sandboxing: Deploy agents in contained environments to prevent cascading errors or unintended cross-system actions.
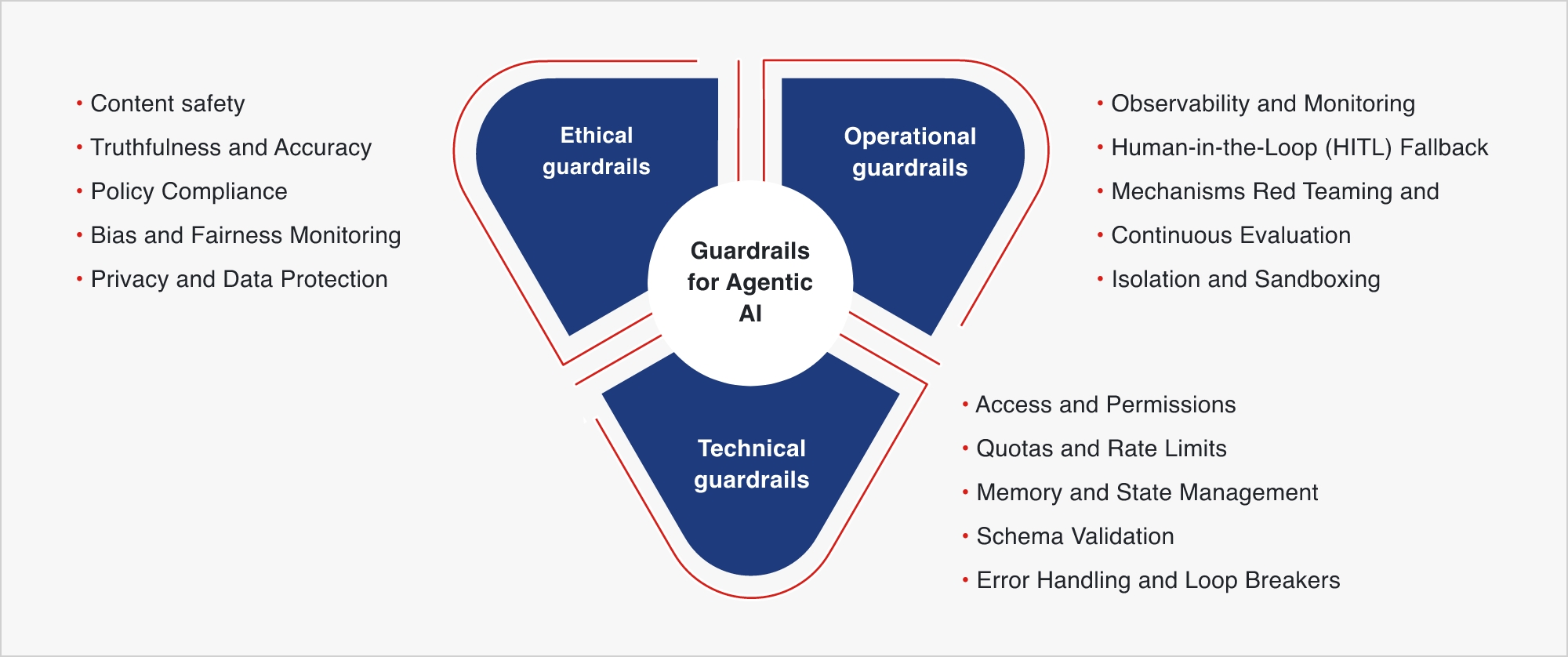
Fig.1. Types of guardrails
How guardrails work
Guardrails function as a multi-layered control system that intercepts, evaluates, and corrects outputs before they reach end users or trigger downstream actions. They use a blend of deterministic rules (rules, filters, policy constraints) and adaptive AI techniques (classifiers, semantic validators, grounding models) to enforce reliability.
A strong guardrail framework typically includes four interdependent components:
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Evaluator | Acts as the first checkpoint by scanning AI outputs for issues such as inaccuracies, inconsistencies, prohibited content, policy violations, or bias. |
| Refiner | Improves or regenerates outputs flagged by the evaluator like editing language, correcting errors, or grounding responses in factual or approved information. |
| Coordinator | Manages the workflow between evaluators and refiners, determines whether additional corrections are needed and iterates until the output meets all requirements or reaches a defined limit. |
| Supervisor | Oversees the full process including by triggering the guardrail sequence, consolidating logs, monitoring performance trends, and validating that the final output is acceptable. |
Together, these elements create a closed feedback loop that ensures every AI action is safe, consistent, and auditable before it reaches the end user or a production system.
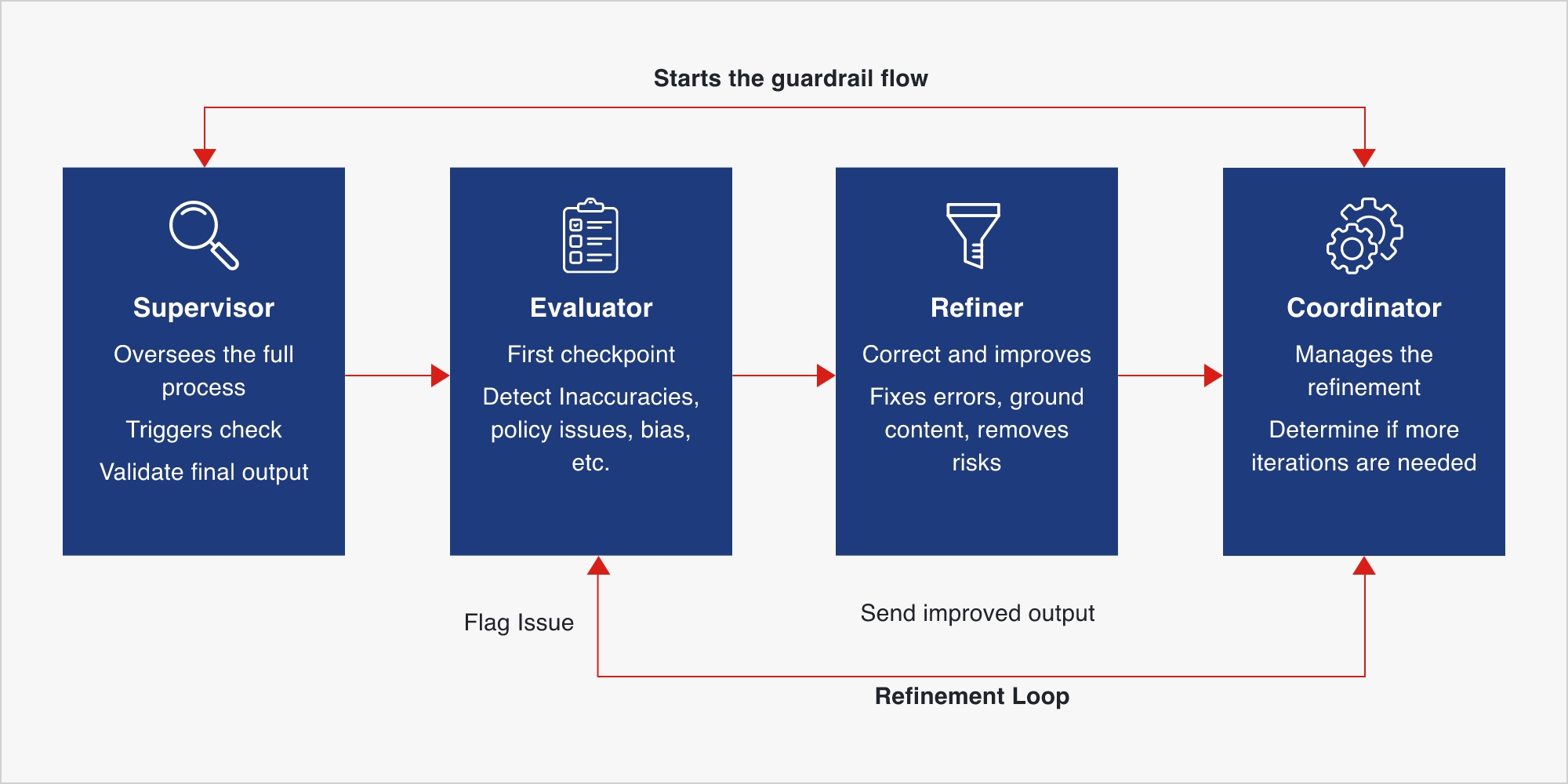
Fig.2. Four components of a guardrail framework
Best practices for deploying guardrails
Establishing guardrails is not just a technical exercise; it’s an organizational capability that requires governance, collaboration, and foresight. For enterprise leaders, the goal is to make guardrails a strategic component of AI design and deployment, not an afterthought.
- Develop guardrail policies collaboratively, bringing together data science, legal, compliance, and business teams to ensure alignment with real operational and regulatory risks.
- Define clear, measurable standards for evaluating guardrail performance, including safety, factual grounding, and bias reduction metrics.
- Create modular, reusable guardrail components that can be easily applied and adapted across multiple AI applications and workflows.
- Continuously monitor model behavior and use adaptive thresholds to account for evolving patterns in agent decision-making.
- Anchor guardrail design to recognized governance frameworks such as NIST AI RMF and ISO/IEC 42001 to maintain regulatory readiness.
- Establish dedicated AI assurance capabilities, including red teaming, model validation, and observability, to provide ongoing oversight and resilience.
Conclusion
Agentic AI represents the next frontier of enterprise automation, where intelligent agents can reason, plan, and act independently. Yet, autonomy without assurance can erode trust faster than it creates value.
Guardrails are not constraints; they are the framework of trust that allows enterprises to scale AI innovation safely. As agentic AI becomes embedded across enterprise workflows, the ability to design, monitor, and evolve guardrails will define industry leaders.
Sigmoid partners with leading organizations to operationalize agentic AI with robust AI governance frameworks, LLMOps expertise, and responsible AI engineering practices so enterprises can scale autonomy.
Featured blogs
Subscribe to get latest insights
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI
Featured blogs
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI








