Exploring the Next Generation of AI-Powered Facial Recognition Technology
Reading Time: 6 minutes
In 2017, face detection technology made its mainstream debut as a feature in smartphones — most notably Apple’s Face ID. Today, AI facial recognition technology has evolved into a powerful tool, integrated across industries and everyday life. This technology has been adopted by major financial institutions, credit card companies, global technology platforms, and even organizations like Major League Baseball. During the pandemic, enterprises upgraded their access control systems by replacing traditional badge or fingerprint readers with AI-powered facial recognition systems. This shift was crucial in decentralized workplaces, where enhancing safety and security in less populated environments became a top priority.
As per a global market study, the facial recognition solution market is soaring. In 2020, its value was nearly $4 billion and is projected to reach $16.74 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 16%. The technology now powers diverse applications — from strengthening security and surveillance to enabling personalized retail experiences and even helping diagnose medical conditions.
Face detection and recognition: Facets of computer vision
Before exploring popular use cases, it’s important to understand the fundamental differences between face detection and recognition, both pillars of computer vision.
1. Face Detection
Face detection is a computer vision technique used to locate and identify human faces within digital images or videos. A face detection algorithm involves analyzing an image or video frame and identifying regions that contain facial features such as eyes, nose, mouth, and the shape of the face. Once the region containing the face is detected, a bounding box is typically drawn around the face for further analysis or processing.
2. Face Recognition
Face recognition is a computer vision technique used to identify or verify the identity of an individual by comparing their facial features with those stored in a database. It involves analyzing an image or video frame, detecting the presence of a face, and extracting specific facial features such as the distance between the eyes, the shape of the jawline, and the curvature of the lips. These features are then compared with the features of previously stored faces to identify the individual.
Prominent facial detection and recognition models
There are several face detection and recognition models that exist today. Some of the most popular ones are:
1. Viola-Jones Algorithm
One of the oldest and most widely used algorithms, it uses Haar cascades and AdaBoost to detect faces in images and video frames.
2. Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)
Another popular face detection algorithm that uses gradient orientations to detect faces in images and video frames.
3. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Currently, the most widely used face recognition models utilizes deep learning models including Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks (MTCNN), Faster R-CNN, FaceNet, VGG-Face, and OpenFace, which are suited for real-time applications like surveillance, eCommerce personalization, and identity verification.
Challenges with existing facial recognition solutions
While the existing face detection and recognition models have shown an optimal level of accuracy, they still have some limitations, such as:
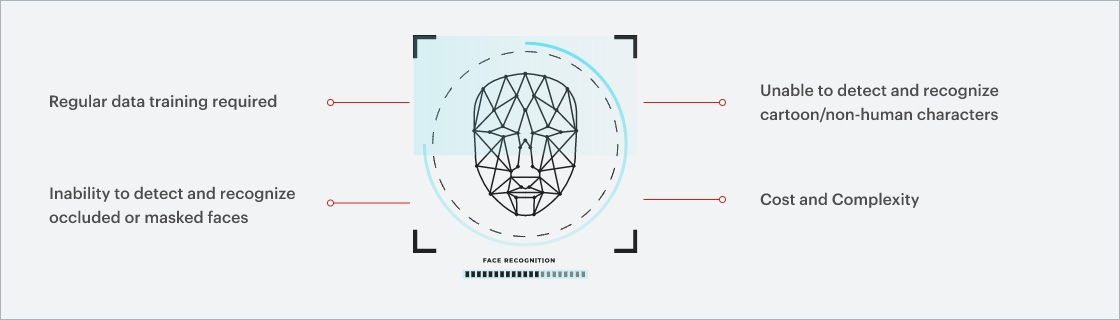
1. Regular data training required
High-accuracy face detection and recognition models require large, diverse datasets that contain images of faces captured under various lighting, poses, and expressions. Obtaining such datasets can be challenging, especially when dealing with data containing facial images of individuals.
2. Inability to detect and recognize occluded or masked faces
Face detection and recognition solutions depend on recognizing clearly visible facial features such as eyes, nose, mouth, and chin. When a face is partially covered or occluded with objects such as hat, glasses or a hand, the facial features may not be easily recognizable, leading to inaccurate or incomplete recognition.
3. Unable to detect and recognize cartoon/non-human characters
Detecting and recognizing non-human faces, such as cartoon characters or animals, is a challenge because their facial features may not conform to typical human features.
4. Cost and Complexity
Developing and implementing advanced facial recognition AI systems can be expensive and time-consuming, requiring significant resources and expertise, which can limit their accessibility to smaller organizations or communities.
Advanced facial recognition technology and its applications
Sigmoid has developed a next-generation AI facial recognition solution that addresses these shortcomings by leveraging deep learning and advanced algorithms requiring minimal training data.
Here are some of the features of Sigmoid’s solution:
- Detects and recognizes both human and non-human faces, even when partially masked or occluded.
- Requires as few as 50–150 images per subject to achieve high accuracy.
- Processes diverse datasets to ensure consistent performance across use cases.
- Recognizes faces at various angles, including side profiles, with strong confidence.
- Provides live detection and labeling via bounding boxes for real-time analysis.
- Generates output video in under 70 minutes for a 44-second input video using standard resources.
These capabilities make it ideal for enterprises looking to adopt scalable, AI-powered facial recognition systems across industries. This is enabled through a proprietary solution framework, as shown in the figure below –
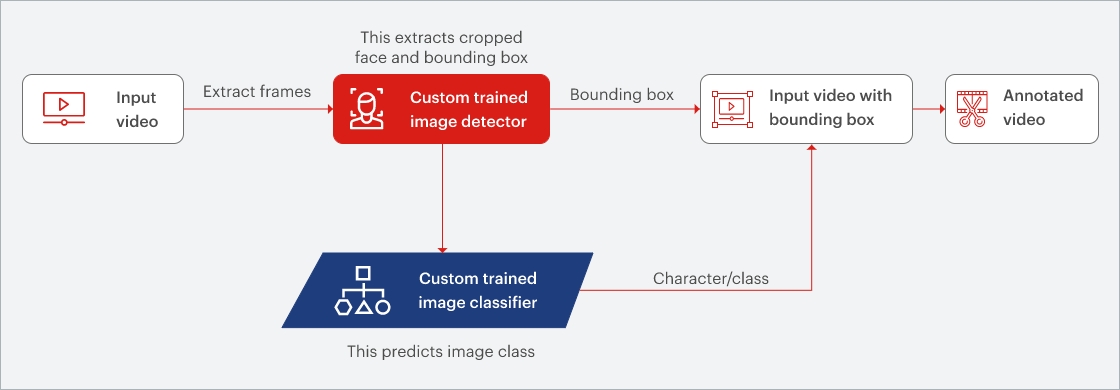
Sigmoid’s facial recognition solution framework
Potential business applications of Sigmoid’s facial recognition solution across industries:
1. Media and Entertainment industry
Face detection and recognition can be used to calculate an actor’s screen time in a movie or TV show, which enables researchers to analyze patterns and correlations between screen time, movie ratings, and box office collection. This information is useful in predicting a movie’s potential success and making casting decisions. Additionally, streaming companies can use this technology to gain insights into viewers’ preferences and provide a more engaging and personalized viewing experience.
2. Financial services
Customer identification and verification can be done through facial recognition. Similarly, facial recognition technology can make the customer onboarding process faster. To reduce ATM robberies or banking fraud cases, facial recognition can be used to add another layer of security.
3. Hospitality
Hotels can use this technology to identify guests, access their reservation information, and provide personalized services based on their preferences. The technology also enables staff to add charges for services accessed during their stay to the guest’s bill.
4. Healthcare
Facial recognition in healthcare can automatically scan a patient’s face and extract medical history and insurance information, saving time for healthcare workers and patients. A recent study shows 66% of patients accept the use of facial recognition technology for this purpose. It can also assist in diagnosing medical disorders in patients with mild or difficult-to-detect symptoms.
5. Retail
Facial recognition in retail stores powers contactless payments, personalized promotions, and tailored customer service. It also strengthens loss prevention by identifying shoplifting patterns in real time.
Why AI Facial Recognition is the future
Neural networks and advanced facial recognition AI have revolutionized detection accuracy, even in challenging conditions like poor lighting, occlusions, or diverse camera angles. Vendors are also prioritizing ethics and privacy by building bias-reduction techniques and secure data governance into their solutions.
From personalized customer engagement to medical diagnostics, AI facial recognition has moved from being a niche technology to a mainstream necessity. With technical breakthroughs, increasing consumer trust, and industry-wide normalisation, 2023–2025 is poised to mark its most significant adoption period yet.
Conclusion
The future of facial recognition lies in AI-powered facial recognition systems that are accurate, ethical, and scalable. As industries embrace digital transformation, these solutions will play a pivotal role in enhancing security, personalization, and operational efficiency across retail, healthcare, finance, and beyond.
Sigmoid’s next-generation facial recognition solution delivers unmatched precision and adaptability, enabling businesses to unlock new opportunities and confidently embrace this transformative technology.
About the authors
Debapriya Das is a Principal Data Scientist at Sigmoid with 11 years of experience across retail, supply chain and marketing analytics. With his deep expertise in data strategy, advanced analytics and unstructured data problems, he has delivered business value to leading Fortune 500 brands and many E-Commerce companies.
Abhishek Verma is a Senior Data Scientist with more than 2 years of experience in the Data Science field. He holds a proven record of delivering successful projects in various domains, such as Customer Relationship Management, Product Development and Computer Vision.
Featured blogs
Subscribe to get latest insights
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI
Featured blogs
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI








